
Male cones make pollen, which is carried to female cones by the wind. Next time you pick up a pine cone, look for loose seeds inside. Gymnosperms are seed plants but their seeds are held in cones. spore-bearing plant, the sporophyte, with a diploid chromosome number, lives. We all know the showy flowers of native kōwhai, flax and pōhutakawa and all those lovely coloured flowers in our gardens, but the tall toetoe and the grasses in our lawns are also flowering plants. New Zealand has about 2,000 native angiosperms, and an amazing 25,000 introduced species found mainly in gardens, farms and orchards.įlowering plants are all around us, even if sometimes we don’t recognise them as having flowers. Fruit can be soft like oranges or hard like nuts.įlowering plants form the biggest group of seed plants, with about 300,000 species around the world – that’s 90% of the whole plant kingdom. In most angiosperms, part of the flower develops into fruit, which protects the seeds inside them. The ovules develop into seeds from which new plants will grow. Pollen is carried from a male part to a female part by wind, insects or other animals (a process called pollination), where it releases male gametes that fertilise the female gametes in the ovules. In the summer, mosses and liverworts make spore capsules. Some plants have these male and female parts in different flowers. Are non-vascular do NOT have a vascular system for conducting water and minerals around the plant, which means they cannot grow very big. They contain male parts that make pollen and female parts that contain ovules. The flowers are special structures for reproduction.
.png)
To assess the importance of these differences, we investigated patterns of species richness and species composition for the native bryophyte, fern, and seed plant floras of the California Channel Islands. Angiosperms – seed plants with flowersĪngiosperms have flowers. Spore-bearing and seed-bearing plants differ in their ability to colonize islands from mainland sources. Plants that hold their seeds in cones are called gymnosperms.

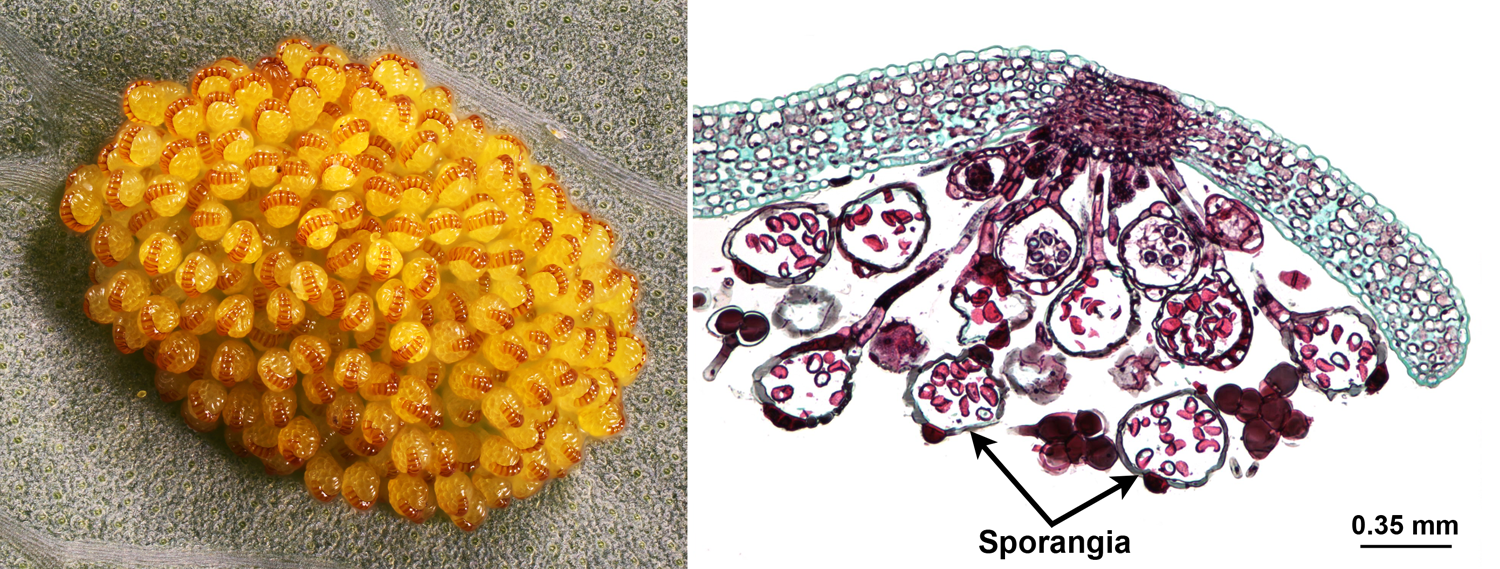
Plants that have flowers are called angiosperms. Common ferns include cinnamon stick, staghorn, horsetails, wisk. Unlike the algae’s and mosses, which disperse spores via spore bearing stalks, most ferns simply have a spore bearing capsule included on certain or even every leaf. They also have special names for these groups. Ferns are the most popular of spore bearing plants and people often use them to adorn their gardens and homes. Scientists divide seed plants into two main groups: plants with flowers and plants with cones. If the seed lands where the conditions are right, the embryo germinates and grows into a new plant. The parent plant disperses or releases the seed. Heterosporous plants produce two kinds of spores megaspores and microspores which are female and male, respectively.

Conversely, a pteridophyte that produces two types of spores is called heterosporous. The seed protects the embryo and stores food for it. Homosporous plants produce only one type of spore that contains both male and female parts. After fertilisation, a tiny plant called an embryo is formed inside a seed. \): This chart shows the geological time scale, beginning with the Pre-Archean eon 3800 million years ago and ending with the Quaternary period in present time.Seed plants have special structures on them where male and female cells join together through a process called fertilisation. Plants follow an alternation of generation life cycle, where diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores and ultimately gives rise to haploid gametophyte.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
